Atmospheric composition and climate: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ComponentTemplate2 | {{ComponentTemplate2 | ||
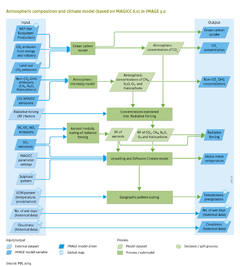
|IMAGEComponent=Crop and grass; Natural vegetation and carbon cycle; Emissions; Climate policy; Air pollution and energy policies; Land and biodiversity policies; Nutrient balances; Hydrological cycle; Human development; | |IMAGEComponent=Crop and grass; Natural vegetation and carbon cycle; Emissions; Climate policy; Air pollution and energy policies; Land and biodiversity policies; Nutrient balances; Hydrological cycle; Human development; | ||
|ExternalModel= | |ExternalModel=LPJmL model; MAGICC model | ||
|KeyReference=Van Vuuren and Stehfest, 2013; Meinshausen et al., 2011a; Meinshausen et al., 2011b; Müller et al., a (unpublished); Van Vuuren et al., 2011; | |KeyReference=Van Vuuren and Stehfest, 2013; Meinshausen et al., 2011a; Meinshausen et al., 2011b; Müller et al., a (unpublished); Van Vuuren et al., 2011; | ||
|Reference=IPCC, 2007a; | |Reference=IPCC, 2007a; | ||
|InputVar=Terrestrial C balance; BC, OC, NOx emissions; SO2 emission; CO, NMVOC emissions; Non CO2 GHG emissions (CH4, N2O, Halocarbon); CO2 emission from energy and industry; Terrestrial CO2 emission - grid; NEP (net ecosystem production) - grid; Nr of wet days - grid; Cloudiness - grid; | |InputVar=Terrestrial C balance; BC, OC, NOx emissions; SO2 emission; CO, NMVOC emissions; Non CO2 GHG emissions (CH4, N2O, Halocarbon); CO2 emission from energy and industry; Terrestrial CO2 emission - grid; NEP (net ecosystem production) - grid; Nr of wet days - grid; Cloudiness - grid; | ||
|Parameter=MAGICC parameter settings; Radiative forcing factors; CGM pattern (temperature, precipitation) - grid; Sulphate pattern - grid; | |Parameter=MAGICC parameter settings; Radiative forcing factors; CGM pattern (temperature, precipitation) - grid; Sulphate pattern - grid; | ||
|OutputVar=CO2 concentration; Non CO2 GHG concentrations; CO2 concentration; Radiative forcing; Global mean temperature; Temperature - grid; Precipitation - grid; Ocean carbon uptake; Nr of wet days - grid; Cloudiness - grid; | |||
|Description=Climate change is considered to be one of impacts of human interference on the environment. Emissions from fossil fuels, industry, land use and land-use change have increased greenhouse gas ([[HasAcronym::GHG]]) concentrations and led to almost 1 oC rise in global mean temperature on pre-industrial levels ([[IPCC, 2007a]]). The impacts are already visible and are expected to increase in the coming century. Without further action, mean global temperature could increase by 4 to 6 °C by the end of this century ([[IPCC, 2007a]]). Climate change impacts manifest themselves in all world regions, and practically affect all aspects of human activity. | |Description=Climate change is considered to be one of impacts of human interference on the environment. Emissions from fossil fuels, industry, land use and land-use change have increased greenhouse gas ([[HasAcronym::GHG]]) concentrations and led to almost 1 oC rise in global mean temperature on pre-industrial levels ([[IPCC, 2007a]]). The impacts are already visible and are expected to increase in the coming century. Without further action, mean global temperature could increase by 4 to 6 °C by the end of this century ([[IPCC, 2007a]]). Climate change impacts manifest themselves in all world regions, and practically affect all aspects of human activity. | ||
Revision as of 18:42, 24 February 2014
Parts of Atmospheric composition and climate
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
| References |
Key policy issues
- What would be the impact of global climate change in this century without additional mitigation policies and measures?
- To what extent would the various scenarios to significantly reduce net greenhouse gas emissions lead to a reduction in climate change?
- To what extent does the uncertainty of geographical patterns in temperature and precipitation change influence future climate impacts and response strategies?