Atmospheric composition and climate: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
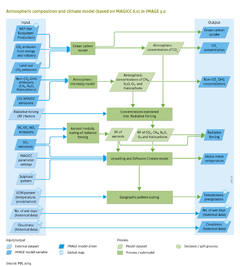
{{ComponentTemplate2 | {{ComponentTemplate2 | ||
|Application=Representative Concentration Pathways - RCP (2009); | |Application=Representative Concentration Pathways - RCP (2009); | ||
|IMAGEComponent=Crops and grass; Carbon cycle and natural vegetation; Emissions; Climate policy; Air pollution and energy policies; Land and biodiversity policies; Nutrients; Water; Human development; | |IMAGEComponent=Crops and grass; Carbon cycle and natural vegetation; Emissions; Climate policy; Air pollution and energy policies; Land and biodiversity policies; Nutrients; Water; Human development; | ||
|ExternalModel=LPJmL model; | |ExternalModel=LPJmL model; | ||
|KeyReference=Van Vuuren and Stehfest, 2013; Meinshausen et al., 2011b; Müller et al., in preparation; | |KeyReference=Van Vuuren and Stehfest, 2013; Meinshausen et al., 2011b; Müller et al., in preparation; | ||
|Reference=IPCC, 2007a; | |Reference=IPCC, 2007a; IPCC, 2013; Meinshausen et al., 2011a; | ||
|InputVar=BC, OC and NOx emissions; SO2 emissions; CO and NMVOC emissions; Non-CO2 GHG emissions (CH4, N2O and Halocarbons); CO2 emission from energy and industry; Land-use CO2 emissions - grid; NEP (net ecosystem production) - grid; Number of wet days - grid; Cloudiness - grid; | |InputVar=BC, OC and NOx emissions; SO2 emissions; CO and NMVOC emissions; Non-CO2 GHG emissions (CH4, N2O and Halocarbons); CO2 emission from energy and industry; Land-use CO2 emissions - grid; NEP (net ecosystem production) - grid; Number of wet days - grid; Cloudiness - grid; | ||
|Parameter=MAGICC parameter settings; Radiative forcing factors; GCM pattern (temperature, precipitation) - grid; Sulphate pattern - grid; | |Parameter=MAGICC parameter settings; Radiative forcing factors; GCM pattern (temperature, precipitation) - grid; Sulphate pattern - grid; | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
There is still considerable uncertainty in climate change simulations, as illustrated by differences in results from various AOGCMs, in terms of mean global temperature, and even more so in geographical patterns of surface temperature and precipitation. By adjusting the values of a few of the model parameters, MAGICC6.0 can reproduce time-dependent responses of AOGCMs ([[Meinshausen et al., 2011a]]; [[Meinshausen et al., 2011b]]). This allows IMAGE to reflect the uncertainty in {{abbrTemplate|AOGCM}} results, and to provide plausible projections of future climate-change feedbacks and impacts. | There is still considerable uncertainty in climate change simulations, as illustrated by differences in results from various AOGCMs, in terms of mean global temperature, and even more so in geographical patterns of surface temperature and precipitation. By adjusting the values of a few of the model parameters, MAGICC6.0 can reproduce time-dependent responses of AOGCMs ([[Meinshausen et al., 2011a]]; [[Meinshausen et al., 2011b]]). This allows IMAGE to reflect the uncertainty in {{abbrTemplate|AOGCM}} results, and to provide plausible projections of future climate-change feedbacks and impacts. | ||
The analysis of climate impacts and feedbacks requires only location-specific temperature and precipitation changes. Thus, a pattern scaling technique is applied in IMAGE by combining MAGICC results with maps on climate change from the same AOGCMs assessed in {{abbrTemplate|AR}}4 ([[IPCC, 2007a]]) and used for calibrating MAGICC. The consistent combination of AOGCM-specific parameter settings for MAGICC and matching geographical patterns of climate change make the dynamic results from IMAGE physically more consistent, and extend the range of uncertainties that can be covered to include future climate change. | The analysis of climate impacts and feedbacks requires only location-specific temperature and precipitation changes. Thus, a pattern scaling technique is applied in IMAGE by combining MAGICC results with maps on climate change from the same AOGCMs assessed in {{abbrTemplate|AR}}4 ([[IPCC, 2007a]]) and used for calibrating MAGICC. The consistent combination of AOGCM-specific parameter settings for MAGICC and matching geographical patterns of climate change make the dynamic results from IMAGE physically more consistent, and extend the range of uncertainties that can be covered to include future climate change. | ||
|ComponentCode=ACC | |ComponentCode=ACC | ||
|AggregatedComponent=Earth System | |AggregatedComponent=Earth System | ||
|FrameworkElementType=state component | |FrameworkElementType=state component | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 18:54, 20 May 2014
Parts of Atmospheric composition and climate
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
| References |
Key policy issues
- What would be the impact of global climate change in this century without additional mitigation policies and measures?
- To what extent would the various scenarios to significantly reduce net greenhouse gas emissions lead to a reduction in climate change?
- To what extent does the uncertainty of geographical patterns in temperature and precipitation change influence future climate impacts and response strategies?