Emissions/Policy issues: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ComponentPolicyIssueTemplate | {{ComponentPolicyIssueTemplate | ||
|Reference=PBL, 2012; | |Reference=PBL, 2012; | ||
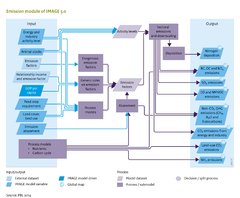
|Description=In a baseline scenario, the emissions of most greenhouse gases typically tend to increase driven by an increase in underlying activity levels. This is shown in | |Description=In a baseline scenario, the emissions of most greenhouse gases typically tend to increase driven by an increase in underlying activity levels. This is shown in the figure below for a baseline scenario developed in 2012 for the [[Roads from Rio+20 (2012) project|Rio+20 study]] ([[PBL, 2012]]). For air pollutants, the typical pattern depends also strongly on the assumptions for air pollution control. In most baseline scenarios, emissions of several air pollutants tend to decrease or at least stabilizse in the next decades as a result of successful tightening of environmental standards in high and middle income countries. | ||
|Example=In the figure below we compare for the air pollutants SO2 and NOx the impacts of introducing more ambitious air pollution control policies (CLE versus EKC) and the influence of climate policy. Wherile climate policy is particularly effective in reducing SO2 emissions, air pollution control policies are effective in reducing NOx emissions. | |Example=In the figure below we compare for the air pollutants SO2 and NOx the impacts of introducing more ambitious air pollution control policies (CLE versus EKC) and the influence of climate policy. Wherile climate policy is particularly effective in reducing SO2 emissions, air pollution control policies are effective in reducing NOx emissions. | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 15:11, 15 January 2014
Parts of Emissions/Policy issues
| Component is implemented in: |
Components:and
|
| Projects/Applications |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
| References |