Human development: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
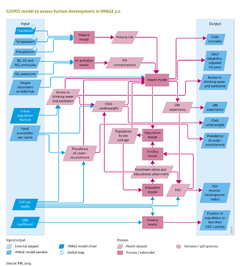
|Description=The environment is important for human development and quality of life, especially for people in developing countries. People’s livelihoods are based on the quantity and quality of the resources they have access to. Unequal access and diminished resource quality have an unequivocal effect on these livelihoods, with negative health impacts as one of the main factors. As seen in the preceding sections, rising demand for food, water and energy will put pressure on scarce natural resources, such as fertile land, potable water and forest resources. The provision of food, water, and energy becomes more difficult when these natural resources are not properly managed or when they degrade due to global environmental change. | |Description=The environment is important for human development and quality of life, especially for people in developing countries. People’s livelihoods are based on the quantity and quality of the resources they have access to. Unequal access and diminished resource quality have an unequivocal effect on these livelihoods, with negative health impacts as one of the main factors. As seen in the preceding sections, rising demand for food, water and energy will put pressure on scarce natural resources, such as fertile land, potable water and forest resources. The provision of food, water, and energy becomes more difficult when these natural resources are not properly managed or when they degrade due to global environmental change. | ||
The Global Integrated Sustainability Model ([[GISMO model]]) addresses (changes in) human development, including the distribution of access to sanitation, food and energy, and of the related changes in economic, social and environmental areas ([[Hilderink and Lucas, 2008]]). Among other things, the model quantifies human development in terms of access to food, water and energy, the Human Development Index (HDI), Population Health measures (e.g. child mortality and life expectancy), and many indicators of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). | The Global Integrated Sustainability Model ([[GISMO model]]) addresses (changes in) human development, including the distribution of access to sanitation, food and energy, and of the related changes in economic, social and environmental areas ([[Hilderink and Lucas, 2008]]). Among other things, the model quantifies human development in terms of access to food, water and energy, the Human Development Index ([[HDI]]), Population Health measures (e.g. child mortality and life expectancy), and many indicators of the Millennium Development Goals ([[MDG|MDGs]]). | ||
Here we concentrate on those parts of GISMO that link directly to other parts of the main IMAGE model, namely climate-related health risks, health problems related to urban and indoor air pollution, and the effects of malnutrition. On all scales, from global UN processes to local initiatives, decision-makers are concerned with improving the standard of living and human development. The IMAGE framework provides valuable insights into key environmental factors that affect human development, and how these impacts may be reduced by improving the natural environment. | Here we concentrate on those parts of GISMO that link directly to other parts of the main IMAGE model, namely climate-related health risks, health problems related to urban and indoor air pollution, and the effects of malnutrition. On all scales, from global UN processes to local initiatives, decision-makers are concerned with improving the standard of living and human development. The IMAGE framework provides valuable insights into key environmental factors that affect human development, and how these impacts may be reduced by improving the natural environment. | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 18:19, 10 December 2013
Parts of Human development
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
Key policy issues
- What are the key future trends in human development, such as those targeted by the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs)?
- How are changes in the global environment likely to affect human development?
- How is improved access to food, water and energy likely to contribute to human development?