Human development/Description: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "HDI" to "HDI (human development index)|HDI") |
m (Text replace - "HDI" to "HDI (human development index)|HDI") |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ComponentDescriptionTemplate | {{ComponentDescriptionTemplate | ||
|Reference=Hilderink, 2000; UNDP, 1990; UNDP, 2010; WHO, 2002; Cairncross and Valdmanis, 2006; Mathers and Loncar, 2006; Craig et al., 1999; Smith and Haddad, 2000; De Onis and Blossner, 2003; FAO, 2003; Mathers and Loncar, 2006; Pandey et al., 2006; Dockery et al., 1993; Pope et al., 1995; Ravallion et al., 2008; | |Reference=Hilderink, 2000; UNDP, 1990; UNDP, 2010; WHO, 2002; Cairncross and Valdmanis, 2006; Mathers and Loncar, 2006; Craig et al., 1999; Smith and Haddad, 2000; De Onis and Blossner, 2003; FAO, 2003; Mathers and Loncar, 2006; Pandey et al., 2006; Dockery et al., 1993; Pope et al., 1995; Ravallion et al., 2008; | ||
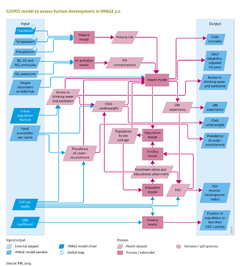
|Description=In the GISMO model, the impacts of global environmental change on human development are modelled by considering impacts on human health – either directly, for example, via the impact of climate change on malaria, or indirectly, such as by the impact of climate change on food availability. In addition to environmental factors, human health is also driven by socioeconomic factors, including income levels and educational attainment. To take account of these different factors and their interrelation, the GISMO model consists of three modules that address human health, poverty and education (see Figure on the right). The modules are linked through a cohort component population model, including endogenous fertility and mortality (for details see [[Hilderink, 2000]]). Fertility levels are modelled using a convergence level that is determined by female educational levels, and a speed of convergence, determined by the human development index ([[HDI (human development index)|HDI]]) (see below). Mortality rates are determined by the health module, which is discussed in further detail in the remainder of this section. Future trends in migration, including urbanisation, are put exogenously into the model (for details see [[Hilderink, 2000]]) | |Description=In the GISMO model, the impacts of global environmental change on human development are modelled by considering impacts on human health – either directly, for example, via the impact of climate change on malaria, or indirectly, such as by the impact of climate change on food availability. In addition to environmental factors, human health is also driven by socioeconomic factors, including income levels and educational attainment. To take account of these different factors and their interrelation, the GISMO model consists of three modules that address human health, poverty and education (see Figure on the right). The modules are linked through a cohort component population model, including endogenous fertility and mortality (for details see [[Hilderink, 2000]]). Fertility levels are modelled using a convergence level that is determined by female educational levels, and a speed of convergence, determined by the human development index ([[HDI (human development index)|HDI (human development index)|HDI (human development index)|HDI]]) (see below). Mortality rates are determined by the health module, which is discussed in further detail in the remainder of this section. Future trends in migration, including urbanisation, are put exogenously into the model (for details see [[Hilderink, 2000]]) | ||
The Human Development Index (HDI (human development index)|HDI), introduced in the UNDP Human Development Report 1990, to rank development achievement is a composite index of life expectancy, education, and income indices ([[UNDP, 1990]];[[UNDP, 2010]]). The underlying indicators have been refined several times, over the years, while the three elements have remained the same. The index links to the three GISMO model components. | The Human Development Index (HDI (human development index)|HDI (human development index)|HDI (human development index)|HDI), introduced in the UNDP Human Development Report 1990, to rank development achievement is a composite index of life expectancy, education, and income indices ([[UNDP, 1990]];[[UNDP, 2010]]). The underlying indicators have been refined several times, over the years, while the three elements have remained the same. The index links to the three GISMO model components. | ||
== GISMO health model == | == GISMO health model == | ||
Revision as of 15:47, 3 February 2014
Parts of Human development/Description
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
| References |