Policy intervention figure Atmospheric composition and climate: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
Oostenrijr (talk | contribs) m (Oostenrijr moved page Policy intervention figure ACC to Policy intervention figure Atmospheric composition and climate without leaving a redirect: Text replace - "ACC" to "Atmospheric composition and climate") |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{FigureTemplate | {{FigureTemplate | ||
|Figure=096x img13.png | |Figure=096x img13.png | ||
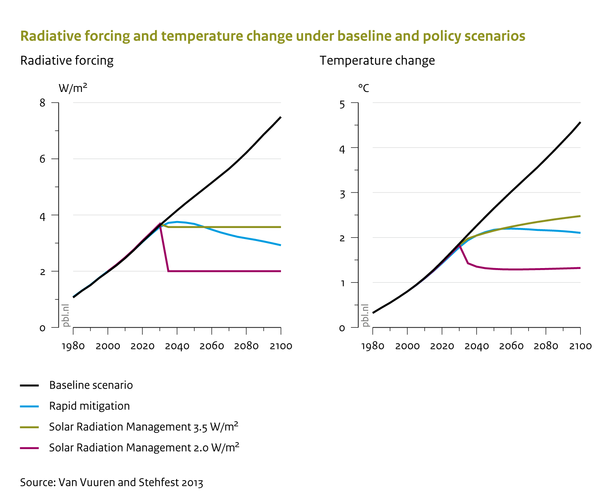
|AltText= | |AltText=Radiative forcing and temperature change under baseline and policy scenarios | ||
|Caption= | |Caption=In addition to ‘conventional’ climate policy, there may be situations where urgent action on climate change is required, either via rapid mitigation, or via Solar Radiation Management (SRM) (e.g. sulphur emissions to the stratosphere). Radiative forcing is immediately stabilised at the intended level by SRM, and also temperatures are adjusted immediately (though not yet at the equilibrium level), and even faster under extreme SRM than would be possible through strong mitigation. However, substantial uncertainties and risks are related to such drastic manipulations of the radiation balance. | ||
|FigureType=Policy intervention figure | |FigureType=Policy intervention figure | ||
|OptimalSize=600 | |OptimalSize=600 | ||
|Component=Atmospheric composition and climate; | |Component=Atmospheric composition and climate; | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 13:53, 24 June 2014

Caption: In addition to ‘conventional’ climate policy, there may be situations where urgent action on climate change is required, either via rapid mitigation, or via Solar Radiation Management (SRM) (e.g. sulphur emissions to the stratosphere). Radiative forcing is immediately stabilised at the intended level by SRM, and also temperatures are adjusted immediately (though not yet at the equilibrium level), and even faster under extreme SRM than would be possible through strong mitigation. However, substantial uncertainties and risks are related to such drastic manipulations of the radiation balance.
Figure is used on page(s): Atmospheric composition and climate