Flood risks/Description: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
ArnoBouwman (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
ArnoBouwman (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ComponentDescriptionTemplate | {{ComponentDescriptionTemplate | ||
|Status=On hold | |Status=On hold | ||
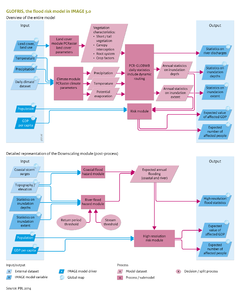
|Description=The purpose of the [[GLOFRIS model]] ([[Winsemius et al., 2012]]) is to estimate the effect of land cover and climate change on flood risks in river catchments and coastal areas on a global level. The global flood risks are expressed in the projected number of people affected, annually, and in GDP value. GLOFRIS uses land-cover input from [[IMAGE land use model|IMAGE]] and climate time series, such as the IPCC GCM projections. These input data drive a global hydrological model ([[PCR-GLOBWB model| PCR-GLOBWB]], the computational core of the module). PCR-GLOBWB calculates where and when flooding events may occur, and calculates the inundation extent and depth needed to estimate flood risks. PCR-GLOBWB has features (daily time steps and proper accounting of the relationship between non-linear soil moisture and run-off) that make this model appropriate for simulating flooding events. The spatial resolution currently used by the model is 0.5 x 0.5 degrees (and 5 x 5 minute resolution, currently under development). The different model steps of the main GLOFRIS module are shown in the | |Description=The purpose of the [[GLOFRIS model]] ([[Winsemius et al., 2012]]) is to estimate the effect of land cover and climate change on flood risks in river catchments and coastal areas on a global level. The global flood risks are expressed in the projected number of people affected, annually, and in GDP value. GLOFRIS uses land-cover input from [[IMAGE land use model|IMAGE]] and climate time series, such as the IPCC GCM projections. These input data drive a global hydrological model ([[PCR-GLOBWB model| PCR-GLOBWB]], the computational core of the module). PCR-GLOBWB calculates where and when flooding events may occur, and calculates the inundation extent and depth needed to estimate flood risks. PCR-GLOBWB has features (daily time steps and proper accounting of the relationship between non-linear soil moisture and run-off) that make this model appropriate for simulating flooding events. The spatial resolution currently used by the model is 0.5 x 0.5 degrees (and 5 x 5 minute resolution, currently under development). The different model steps of the main GLOFRIS module are shown in the model flow diagram of GLOFRIS on the right. | ||
The land-cover map ‘Global Land Cover Characterization’ (GLCC) ([[Loveland et al., 2000]]) is the basis of the parameters of the PCR-GLOBWB hydrological model ( | The land-cover map ‘Global Land Cover Characterization’ (GLCC) ([[Loveland et al., 2000]]) is the basis of the parameters of the PCR-GLOBWB hydrological model (model flow diagram of GLOFRIS on the right). These parameters express the hydrological characteristics of different land-cover types. IMAGE and PCR-GLOBWB are linked by lookup tables that translate the IMAGE land-cover classification into that of GLCC. | ||
The hydrological model PCR-GLOBWB ([[Van Beek et al., 2011]]; [[Wada et al., 2011]]) requires data on daily precipitation, potential evaporation and temperature that are consistent with the IMAGE scenario. Daily data are required because that reflects intermonthly and interannual climate variability and its effect on flood risk. | The hydrological model PCR-GLOBWB ([[Van Beek et al., 2011]]; [[Wada et al., 2011]]) requires data on daily precipitation, potential evaporation and temperature that are consistent with the IMAGE scenario. Daily data are required because that reflects intermonthly and interannual climate variability and its effect on flood risk. | ||
Revision as of 11:49, 9 December 2013
Parts of Flood risks/Description
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
| References |