Flood risks: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "Land cover;" to "Land cover, land use - grid;") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ComponentTemplate2 | {{ComponentTemplate2 | ||
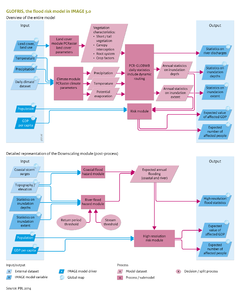
|IMAGEComponent=Scenario drivers;land cover and use;Human development | |IMAGEComponent=Scenario drivers;land cover and use;Human development | ||
|ExternalModel= PCR-GLOBWB model; DIVA model; | |ExternalModel=PCR-GLOBWB model; DIVA model; | ||
|KeyReference=Ward et al., 2013; Winsemius et al., 2012; | |KeyReference=Ward et al., 2013; Winsemius et al., 2012; | ||
|Reference=UNISDR, 2011; | |Reference=UNISDR, 2011; | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
Bierkens and Van Beek, 2009; | Bierkens and Van Beek, 2009; | ||
Hinkel and Klein, 2009; | Hinkel and Klein, 2009; | ||
|InputVar=Land cover, land use - grid | |InputVar=Land cover, land use - grid; Population - grid; GDP per capita - grid; Historical climate dataset - grid; | ||
|OutputVar=River discharge; Flooded depth; Flooded fraction; Affected GDP; GDP and population at risk; | |OutputVar=River discharge; Flooded depth; Flooded fraction; Affected GDP; GDP and population at risk; | ||
|Parameter=Topography - grid; Coastal storm surges; Flood statistics; | |||
|Description=Flooding is the most frequent and costly natural hazard, affecting a majority of countries on a regular basis ([[UNISDR, 2011]]) ([[IPCC, 2012]]). Over the past few decades, the economic damage as a result of flooding has increased in most regions, primarily due to a growth in population and wealth in flood-prone areas ([[Bouwer et al., 2010]]; [[UNISDR, 2011]]; [[Barredo et al., 2012]]). | |Description=Flooding is the most frequent and costly natural hazard, affecting a majority of countries on a regular basis ([[UNISDR, 2011]]) ([[IPCC, 2012]]). Over the past few decades, the economic damage as a result of flooding has increased in most regions, primarily due to a growth in population and wealth in flood-prone areas ([[Bouwer et al., 2010]]; [[UNISDR, 2011]]; [[Barredo et al., 2012]]). | ||
The largest changes in economic loss and mortality from flooding are observed in developing countries, although data scarcities are hampering flood risk assessments. In order to evaluate current flood risk as well as possible changes under global change scenarios, there is a demand for rapid cost-effective assessments based on available global data sets. Such assessments are of interest to various users, for example: | The largest changes in economic loss and mortality from flooding are observed in developing countries, although data scarcities are hampering flood risk assessments. In order to evaluate current flood risk as well as possible changes under global change scenarios, there is a demand for rapid cost-effective assessments based on available global data sets. Such assessments are of interest to various users, for example: | ||
Revision as of 13:39, 3 February 2014
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
| References |
Key policy issues
- How will future flood risk change as a result of socio-economic changes and climate change?
- What would be the impact of floods, in terms of damage and victims, and where are the hot spots?
- What would be suitable adaptation strategies and investment options related to flood risk?