Policy intervention figure Terrestrial biodiversity: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
(CSV import) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{FigureTemplate | {{FigureTemplate | ||
|Figure= | |Figure=100g img13.png | ||
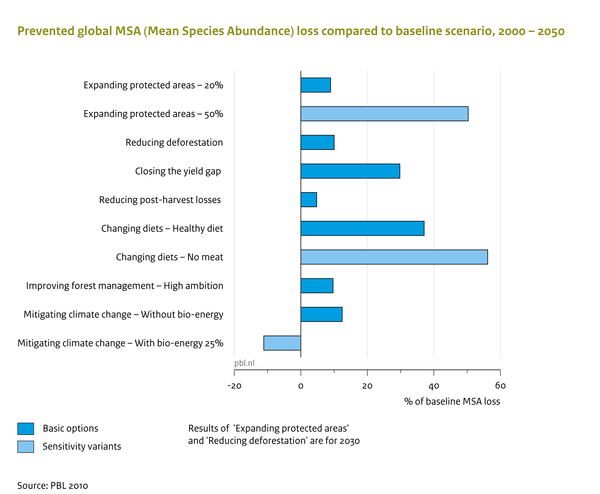
|Caption= | |Caption=Several policy interventions in land-use regulation, production and demand systems could prevent some of the biodiversity loss projected in the baseline. The single largest effects can be expected from closing the yield gap, and from dietary changes. | ||
|FigureType=Policy intervention figure | |FigureType=Policy intervention figure | ||
|OptimalSize=600 | |OptimalSize=600 | ||
|Component=Terrestrial biodiversity; | |Component=Terrestrial biodiversity; | ||
|AltText=Prevented global MSA (Mean Species Abundance) loss compared to baseline scenario, 2000 - 2050 | |||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 14:43, 23 May 2014

Caption: Several policy interventions in land-use regulation, production and demand systems could prevent some of the biodiversity loss projected in the baseline. The single largest effects can be expected from closing the yield gap, and from dietary changes.
Figure is used on page(s): Terrestrial biodiversity