Carbon cycle and natural vegetation/Description: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|Reference=Prentice et al., 2007; | |Reference=Prentice et al., 2007; | ||
|Description=<h3>Vegetation types</h3> | |Description=<h3>Vegetation types</h3> | ||
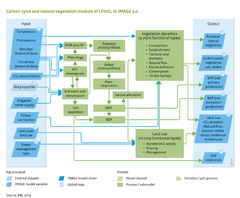
LPJmL is a Dynamic Global Vegetation Model (abbrTemplate|DGVM | LPJmL is a Dynamic Global Vegetation Model ({{abbrTemplate|DGVM}}) that was developed initially to assess the role of the terrestrial biosphere in the global carbon cycle ([[Prentice et al., 2007]]). DGVMs simulate vegetation distribution and dynamics, using the concept of multiple plant functional types ({{abbrtemplate|PFT}}s) differentiated according to their bioclimatic (e.g. temperature requirement), physiological, morphological, and phenological (e.g. growing season) attributes, and competition for resources (light and water). | ||
To aggregate the vast diversity of plant species worldwide, with respect to major differences relevant to the carbon cycle, [[LPJmL model|LPJmL]] distinguishes nine plant functional types. These include e.g. tropical evergreen trees, temperate deciduous broad-leaved trees and C3 herbaceous plants. Plant dynamics are computed for each PFT present in a grid cell. As IMAGE uses the concept of biomes, combinations of PFTs in an area/grid cell are translated into a biome type (see [[Plant functional types]]). | To aggregate the vast diversity of plant species worldwide, with respect to major differences relevant to the carbon cycle, [[LPJmL model|LPJmL]] distinguishes nine plant functional types. These include e.g. tropical evergreen trees, temperate deciduous broad-leaved trees and C3 herbaceous plants. Plant dynamics are computed for each PFT present in a grid cell. As IMAGE uses the concept of biomes, combinations of PFTs in an area/grid cell are translated into a biome type (see [[Plant functional types]]). | ||
Revision as of 10:15, 20 May 2014
Parts of Carbon cycle and natural vegetation/Description
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
| References |