Water/Description: Difference between revisions
< Water
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==The ‘natural’ hydrological cycle== | ==The ‘natural’ hydrological cycle== | ||
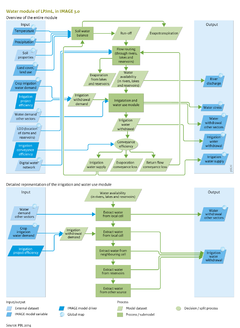
The hydrological module in the LPJmL model consists of a vertical water balance (Gerten et al., 2004) and a lateral flow component ([[Rost et al., 2008]]) (Figure 6.3.1a[[*********]]), which are run at 0.5 degree resolution in time steps of one day. The soil in each grid cell is represented by a two-layer soil column of 0.5 and 1 metre depth, respectively, partly covered with natural vegetation or crops. | The hydrological module in the LPJmL model consists of a vertical water balance ([[Gerten et al., 2004]]) and a lateral flow component ([[Rost et al., 2008]]) (Figure 6.3.1a[[*********]]), which are run at 0.5 degree resolution in time steps of one day. The soil in each grid cell is represented by a two-layer soil column of 0.5 and 1 metre depth, respectively, partly covered with natural vegetation or crops. | ||
The potential evaporation rate in each grid cell depends primarily on net radiation and temperature, and is calculated using the Priestley-Taylor approach ([[Gerten et al., 2004]]). The actual evapotranspiration is calculated as the sum of three components: evaporation of intercepted precipitation, bare soil evaporation and plant transpiration. ([[Gerten et al., 2004]]). | The potential evaporation rate in each grid cell depends primarily on net radiation and temperature, and is calculated using the Priestley-Taylor approach ([[Gerten et al., 2004]]). The actual evapotranspiration is calculated as the sum of three components: evaporation of intercepted precipitation, bare soil evaporation and plant transpiration. ([[Gerten et al., 2004]]). | ||
The water storage in the canopy is a function of vegetation type, leaf area index ([[LAI]]) and precipitation amount. Interception evaporation occurs at potential evaporation rate, during the fraction of the daytime that the canopy is wet. | The water storage in the canopy is a function of vegetation type, leaf area index ([[LAI]]) and precipitation amount. Interception evaporation occurs at potential evaporation rate, during the fraction of the daytime that the canopy is wet. | ||
Revision as of 11:18, 10 December 2013
Parts of Water/Description
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Key publications |
| References |