Energy demand: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
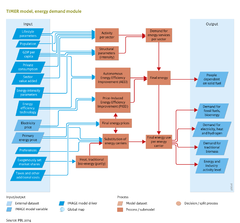
|IMAGEComponent=Energy supply and demand; Energy conversion; Energy supply; | |IMAGEComponent=Energy supply and demand; Energy conversion; Energy supply; | ||
|KeyReference=Daioglou et al., 2012; Girod et al., 2012; Van Ruijven et al., 2012; | |KeyReference=Daioglou et al., 2012; Girod et al., 2012; Van Ruijven et al., 2012; | ||
|InputVar=GDP per capita; Value added; Private consumption; Population per Region; Energy intensity parameters; Energy efficiency technology; Exogenous market shares; Primary energy price; Electricity price; Lifestyle parameters; | |InputVar=GDP per capita; Value added; Private consumption; Population per Region; Energy intensity parameters; Energy efficiency technology; Exogenous market shares; Primary energy price; Electricity price; Lifestyle parameters; | ||
|Parameter=Taxes and other additional costs; Preferences; | |Parameter=Taxes and other additional costs; Preferences; | ||
|OutputVar=Demand for primary energy; Demand for electricity and hydrogen; Demand for traditional biomass; People dependent on solid fuel; | |||
|FrameworkElementType=model component | |FrameworkElementType=model component | ||
|Description=Global final energy demand has increased rapidly since the industrial revolution. While in the past most of the increase occurred in industrialised regions, currently the largest growth occurs in emerging economies and developing regions. Given the legitimate aspiration of income growth in the medium- and low-income countries, one can expect also in the coming decades a high rate of growth in energy demand with important implications for sustainability. Key policy questions are: | |Description=Global final energy demand has increased rapidly since the industrial revolution. While in the past most of the increase occurred in industrialised regions, currently the largest growth occurs in emerging economies and developing regions. Given the legitimate aspiration of income growth in the medium- and low-income countries, one can expect also in the coming decades a high rate of growth in energy demand with important implications for sustainability. Key policy questions are: | ||
Revision as of 12:52, 28 August 2013
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Key publications |
Key policy issues
- How will energy demand evolve particularly in emerging and medium- and low-income economies?
- What is the mix of end-use energy carriers to meet future energy demand?
- How can energy efficiency contribute to reducing the growth rate of energy demand and mitigate pressures on the global environment?
Introduction
"model component" is not in the list (driver component, pressure component, interaction component, state component, impact component, response component) of allowed values for the "FrameworkElementType" property.