Energy supply and demand: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
|ExternalModel=POLES model | |ExternalModel=POLES model | ||
|KeyReference=Van Vuuren, 2007; De Vries et al., 2001; | |KeyReference=Van Vuuren, 2007; De Vries et al., 2001; | ||
|Reference=De Vries et al., 2001; Van Vuuren, 2007; Criqui et al., 2003; Thomson et al. 2011; | |Reference=De Vries et al., 2001; Van Vuuren, 2007; Criqui et al., 2003; Thomson et al., 2011; | ||
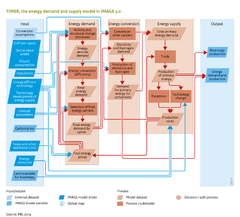
|Description={{DisplayFigureTemplate|flowcart ESD}} | |Description={{DisplayFigureTemplate|flowcart ESD}} | ||
Energy consumption and production constitutes a central component in discussions on sustainable development. First of all, without the use of energy most human activities are impossible. Hence, securing a reliable and affordable supply of fit-for-purpose energy is an important element of countries' economic and energy policies. Fossil-fuel resources currently account for more than three quarters of the world's energy use. However, over time, depletion is expected to lead to rising costs for fossil fuels (at least for oil), while the fossil fuels resources that remain easily accessible will be concentrated in a decreasing number of countries. Finally, the combustion of fossil fuels and traditional forms of bio-energy is the single most important cause of local and regional air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. The future of the global energy system is highly uncertain and depends on factors such as technological innovations and breakthroughs, socio-economic developments, resource availability and societal choices. Exploring different scenarios for developments around the use and supply of energy in the future provides information to decision-makers, on which strategic policy decisions can be based. | Energy consumption and production constitutes a central component in discussions on sustainable development. First of all, without the use of energy most human activities are impossible. Hence, securing a reliable and affordable supply of fit-for-purpose energy is an important element of countries' economic and energy policies. Fossil-fuel resources currently account for more than three quarters of the world's energy use. However, over time, depletion is expected to lead to rising costs for fossil fuels (at least for oil), while the fossil fuels resources that remain easily accessible will be concentrated in a decreasing number of countries. Finally, the combustion of fossil fuels and traditional forms of bio-energy is the single most important cause of local and regional air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. The future of the global energy system is highly uncertain and depends on factors such as technological innovations and breakthroughs, socio-economic developments, resource availability and societal choices. Exploring different scenarios for developments around the use and supply of energy in the future provides information to decision-makers, on which strategic policy decisions can be based. | ||
Revision as of 16:52, 12 December 2013
|
Composition of Energy supply and demand Additional info |
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Projects/Applications |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
| References |
Description of Energy supply and demand