Water: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "|Status=On hold" to "") |
m (Text replace - "Soil and vegetation characteristics" to "Soil characteristics") |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
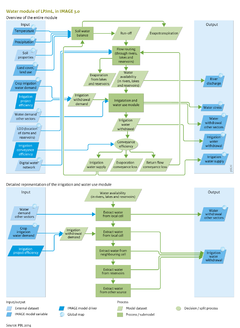
|InputVar=Land cover; Temperature; Precipitation; Crop irrigation water requirement; Irrigation project and conveyance efficiency; Crop irrigation water requirement; | |InputVar=Land cover; Temperature; Precipitation; Crop irrigation water requirement; Irrigation project and conveyance efficiency; Crop irrigation water requirement; | ||
|OutputVar=Water availability; Irrigation water supply; Run off; River flow; Digital water network; | |OutputVar=Water availability; Irrigation water supply; Run off; River flow; Digital water network; | ||
|Parameter=Soil | |Parameter=Soil characteristics; Water demand other sectors; | ||
|Description=Water plays an important role in many natural and human processes. Its availability is essential for natural vegetation and agricultural production, for human settlements and industry. Around one third of the worlds’ population is living in countries already suffering from ‘medium’ to ‘high’ water stress ([[OECD, 2012]]). This number is expected to increase further, due to a growing population that will need more water and is living in a changing climate. | |Description=Water plays an important role in many natural and human processes. Its availability is essential for natural vegetation and agricultural production, for human settlements and industry. Around one third of the worlds’ population is living in countries already suffering from ‘medium’ to ‘high’ water stress ([[OECD, 2012]]). This number is expected to increase further, due to a growing population that will need more water and is living in a changing climate. | ||
Today, agriculture is responsible for 70% of the total global water withdrawals and is thus by far the biggest water user. Around one third of the total global crop production is harvested from irrigated areas, although they only occupy 17% of croplands (e.g. [[Portmann et al., 2010]]). This indicates that irrigation generally supports more productive agricultural practices. | Today, agriculture is responsible for 70% of the total global water withdrawals and is thus by far the biggest water user. Around one third of the total global crop production is harvested from irrigated areas, although they only occupy 17% of croplands (e.g. [[Portmann et al., 2010]]). This indicates that irrigation generally supports more productive agricultural practices. | ||
Revision as of 13:17, 8 January 2014
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Key publications |
| References |
Key policy issues
- What is the combined effect of climate change and socio-economic development on water demand and availability, and on associated agricultural production?
- What is the potential of adaptation measures to reduce water stress and water-related crop production losses?
- How can water demand be reduced and still provide the adequate service levels to the sectors with the highest demand?