Water: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "Crop and grass" to "Crops and grass") |
m (Text replace - "Vegetation, hydrology and agriculture" to "Carbon, vegetation, agriculture and water") |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
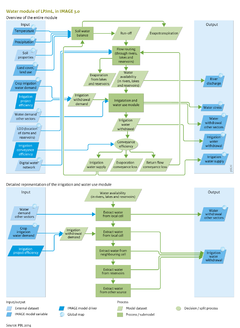
An overview of data exchanges with other IMAGE modules is given below. Data on annual land cover and land use are used as input into LPJmL, including information on the location of irrigated areas and types of crops. This influences the amounts of water that evaporate and run off, as well as the amount of water needed for those irrigated areas. Vice versa, information on water availability as calculated by LPJmL is taken into account by the land allocation model to find suitable locations for the expansion of irrigated areas. Climate is used as an input into LPJmL to determine reference evapotranspiration, and the precipitation input to the water balance ([[Gerten et al., 2004]]). The crop model, which is also part of LPJmL ([[Crops and grass]]), calculates irrigation water demand based on crop characteristics, soil moisture and climate. If the amount of water available for irrigation is limited, the crop model calculates the reduction in crop yield due to water stress. | An overview of data exchanges with other IMAGE modules is given below. Data on annual land cover and land use are used as input into LPJmL, including information on the location of irrigated areas and types of crops. This influences the amounts of water that evaporate and run off, as well as the amount of water needed for those irrigated areas. Vice versa, information on water availability as calculated by LPJmL is taken into account by the land allocation model to find suitable locations for the expansion of irrigated areas. Climate is used as an input into LPJmL to determine reference evapotranspiration, and the precipitation input to the water balance ([[Gerten et al., 2004]]). The crop model, which is also part of LPJmL ([[Crops and grass]]), calculates irrigation water demand based on crop characteristics, soil moisture and climate. If the amount of water available for irrigation is limited, the crop model calculates the reduction in crop yield due to water stress. | ||
|ComponentCode=H | |ComponentCode=H | ||
|AggregatedComponent= | |AggregatedComponent=Carbon, vegetation, agriculture and water | ||
|FrameworkElementType=state component | |FrameworkElementType=state component | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 10:22, 17 May 2014
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Key publications |
| References |
Key policy issues
- What is the combined effect of climate change and socio-economic development on water demand and availability, and on associated agricultural production?
- What is the potential of adaptation measures to reduce water stress and water-related crop production losses?
- How can water demand be reduced and still provide the adequate service levels to the sectors with the highest demand?