Energy supply and demand: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
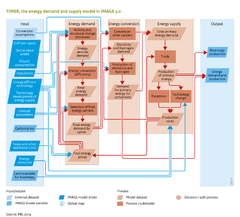
We use the words energy demand and energy use interchageably. However, as far as the past is concerned, data are about statistical energy use. For the future, the trends are in some way extrapolated and denote then energy demand, which is supposed in the model to be fully supplied and is therefore considered to be equal to use. In the subsequent subpages, we discuss different parts of the model in more detail. | We use the words energy demand and energy use interchageably. However, as far as the past is concerned, data are about statistical energy use. For the future, the trends are in some way extrapolated and denote then energy demand, which is supposed in the model to be fully supplied and is therefore considered to be equal to use. In the subsequent subpages, we discuss different parts of the model in more detail. | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[Page has default form:: | [[Page has default form::MainComponentForm]] | ||
[[Category:MainComponent]] | [[Category:MainComponent]] | ||
Revision as of 09:08, 8 August 2013
Parts of Energy supply and demand
- Introduction page
- Overview of references Additional info
- Technical learning
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Projects/Applications |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
| References |
Key policy issues
- How can energy supply and demand become more sustainable, balancing human development, security of supply, and concerns about climate change and air pollution?
- What transitions in the energy system would meet long-term climate goals?
- How are these strategies affected by uncertainties in the energy system?