Energy demand: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
m (Text replace - "Market shares" to "Exogenously set market shares") |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
|KeyReference=Daioglou et al., 2012; Girod et al., 2012; Van Ruijven et al., 2012; | |KeyReference=Daioglou et al., 2012; Girod et al., 2012; Van Ruijven et al., 2012; | ||
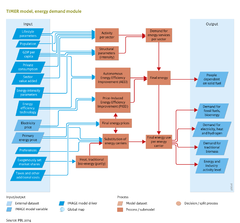
|InputVar=GDP per capita; Sector value added; Private consumption; Population; Energy intensity parameters; Energy efficiency technology; Primary energy price; Electricity price; Lifestyle parameters; | |InputVar=GDP per capita; Sector value added; Private consumption; Population; Energy intensity parameters; Energy efficiency technology; Primary energy price; Electricity price; Lifestyle parameters; | ||
|Parameter=Taxes and other additional costs; Preferences; | |Parameter=Taxes and other additional costs; Preferences;Exogenously set market shares; | ||
|OutputVar=Demand for primary energy; Demand for electricity and hydrogen; Demand for traditional biomass; People dependent on solid fuel; Energy and industry activity level; | |OutputVar=Demand for primary energy; Demand for electricity and hydrogen; Demand for traditional biomass; People dependent on solid fuel; Energy and industry activity level; | ||
|Description=Global final energy use has increased rapidly since the industrial revolution. Although, for a historical perspective, most increases have occurred in currently high-income regions, more recently the largest increase occurred in emerging economies. Given the aspirations for income growth in medium- and low-income countries, a continued high rate of growth in energy demand is to be expected in the coming decades, with important implications for sustainability. | |Description=Global final energy use has increased rapidly since the industrial revolution. Although, for a historical perspective, most increases have occurred in currently high-income regions, more recently the largest increase occurred in emerging economies. Given the aspirations for income growth in medium- and low-income countries, a continued high rate of growth in energy demand is to be expected in the coming decades, with important implications for sustainability. | ||
Revision as of 12:49, 31 March 2014
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Key publications |
Key policy issues
- How will energy demand evolve particularly in emerging and medium- and low-income economies?
- What is the mix of end-use energy carriers to meet future energy demand?
- How can energy efficiency contribute to reducing the growth rate of energy demand and mitigate pressures on the global environment?