Energy supply/Data uncertainties limitations: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
===Limitations=== | ===Limitations=== | ||
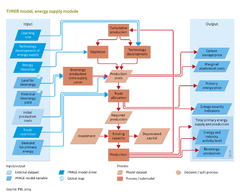
The general limitations of TIMER also apply to energy supply modules with a few specific limitations. As a global model, TIMER specifies resource availability in [[Region classification map|26 global regions]]. However, to some degree this does not take into account the underlying geographical dimensions of individual countries and specific areas. For fossil fuels, this issue leads to heterogeneity within a region (e.g., due to different tax systems), but is more important for renewable energy. A key factor can be transport from one area to another, and calculations require the use of other models. | The general limitations of TIMER also apply to energy supply modules with a few specific limitations. As a global model, TIMER specifies resource availability in [[Region classification map|26 global regions]]. However, to some degree this does not take into account the underlying geographical dimensions of individual countries and specific areas. For fossil fuels, this issue leads to heterogeneity within a region (e.g., due to different tax systems), but is more important for renewable energy. A key factor can be transport from one area to another, and calculations require the use of other models. | ||
Another main limitation concerns the focus on production costs in describing energy markets. Although long-term developments may be expected to be driven by long-term supply costs over the last few decades, issues related to capacity constraints and market formation over longer time periods have lead to fossil fuels prices that differ from production costs. | Another main limitation concerns the focus on production costs in describing energy markets. Although long-term developments may be expected to be driven by long-term supply costs over the last few decades, issues related to capacity constraints and market formation over longer time periods have lead to fossil fuels prices that differ from production costs. | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 16:44, 22 May 2014
Parts of Energy supply/Data uncertainties limitations
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Key publications |
| References |