Energy supply and demand: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "ExternalModel=" to "Model-Database=") |
Oostenrijr (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
===Overview of TIMER=== | ===Overview of TIMER=== | ||
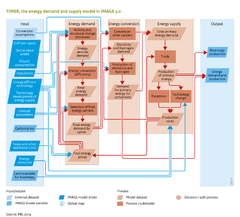
The energy model has three components: energy demand; energy conversion; and energy supply (see | The energy model has three components: energy demand; energy conversion; and energy supply (see Flowchart). The energy demand component describes how energy demand is determined for five economic sectors -industry, transport, residential, services and other sectors. The energy conversion components describes how carriers such as electricity and hydrogen are produced. Finally, the energy supply modules describe the production of primary energy carriers, and calculate prices endogenously for both primary and secondary energy carriers that drive investment in the technologies associated with these carriers. The energy flows in all three main components allow calculation of greenhouse gas and air pollutant emissions. | ||
The energy model TIMER focuses on long-term trends in energy supply and demand. It was mainly developed for analysing climate mitigation strategies and has also been used to explore other sustainability issues. These characteristics impose some limitations on the model. Firstly, the model cannot be used to examine macroeconomic consequences of mitigation strategies, such as GDP losses, because other aspects of the economy are not included. Secondly, the strategies depicted by the model are not necessarily optimal from an inter-temporal perspective because as a simulation model, there is no information on future development in a scenario (myopic). Instead, decisions are made on the basis of available model information at that time in the scenario. Finally, although the model has been used to analyse sustainability issues other than climate change, still much less options have been included to explore such policies (see [[Air pollution and energy policies]]). | The energy model TIMER focuses on long-term trends in energy supply and demand. It was mainly developed for analysing climate mitigation strategies and has also been used to explore other sustainability issues. These characteristics impose some limitations on the model. Firstly, the model cannot be used to examine macroeconomic consequences of mitigation strategies, such as GDP losses, because other aspects of the economy are not included. Secondly, the strategies depicted by the model are not necessarily optimal from an inter-temporal perspective because as a simulation model, there is no information on future development in a scenario (myopic). Instead, decisions are made on the basis of available model information at that time in the scenario. Finally, although the model has been used to analyse sustainability issues other than climate change, still much less options have been included to explore such policies (see [[Air pollution and energy policies]]). | ||
Revision as of 09:10, 24 June 2014
|
Composition of Energy supply and demand Additional info |
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Projects/Applications |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
| References |
Description of Energy supply and demand