Human development/Description: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Oostenrijr (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Oostenrijr (talk | contribs) m (Text replace - "NOx" to "NO<sub>x</sub>") |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
<td>Lung cancer, Cardiopulmonary diseases, Acute respiratory infections (ARI) | <td>Lung cancer, Cardiopulmonary diseases, Acute respiratory infections (ARI) | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
<td>Exposure to PM10 and PM2.5, related to | <td>Exposure to PM10 and PM2.5, related to NO<sub>x</sub>, SO<sub>2</sub> and black carbon emissions | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
====Mortality associated with urban air pollution==== | ====Mortality associated with urban air pollution==== | ||
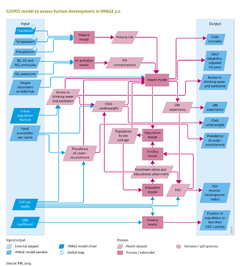
Mortality rates of lung cancer, cardiopulmonary diseases and acute respiratory infections due to urban air pollution (PM10 and PM2.5 concentration levels) are derived using the {{abbrTemplate|GBD}} method ([[Mathers and Loncar, 2006]]). Based on emissions of | Mortality rates of lung cancer, cardiopulmonary diseases and acute respiratory infections due to urban air pollution (PM10 and PM2.5 concentration levels) are derived using the {{abbrTemplate|GBD}} method ([[Mathers and Loncar, 2006]]). Based on emissions of NO<sub>x</sub>, SO<sub>2</sub> and black carbon (Component [[Emissions]]), PM10 concentration levels are determined using the Global Urban Air quality Model ([[GUAM model]]). This model originates from the GMAPS model ([[Pandey et al., 2006]]), which determines PM10 concentration levels by economic activity, population, urbanisation and meteorological factors. PM2.5 concentrations are obtained using a region-specific PM10–PM2.5 ratio. Based on these levels and the exposed population, mortality attributable to causes of death is derived using relative risks obtained from epidemiology studies ([[Dockery et al., 1993]]; [[Pope et al., 1995]]). | ||
===GISMO poverty module=== | ===GISMO poverty module=== | ||
Revision as of 10:38, 1 July 2014
Parts of Human development/Description
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
| References |