Drivers/Scenario drivers: Difference between revisions
< Drivers
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Oostenrijr (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Oostenrijr (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
===Economy=== | ===Economy=== | ||
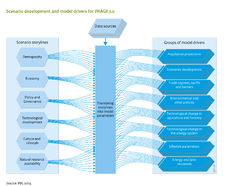
At the most aggregated level, economic activity is described in terms of [[GDP per capita|gross domestic product (GDP) per capita]]. Models outside the IMAGE 3.0 framework, such as the [[ENV-Linkages model|OECD ENV-Growth model]], project long-term GDP growth based on developments in key production factors (e.g., capital, labour, natural resources), and the sector composition of the economy. The various components of GDP on the production side (in particular value added (VA) per sector) and expenditures (in particular private consumption) are estimated with more detailed models that take account of inter-sector linkages, own- and cross-price responses, and other factors [[Chateau et al., 2013]]. | At the most aggregated level, economic activity is described in terms of [[GDP per capita|gross domestic product (GDP) per capita]]. Models outside the IMAGE 3.0 framework, such as the [[ENV-Linkages model|OECD ENV-Growth model]], project long-term GDP growth based on developments in key production factors (e.g., capital, labour, natural resources), and the sector composition of the economy. The various components of GDP on the production side (in particular [[Sector value added|value added (VA) per sector]]) and expenditures (in particular [[private consumption]]) are estimated with more detailed models that take account of inter-sector linkages, own- and cross-price responses, and other factors [[Chateau et al., 2013]]. | ||
In IMAGE 3.0, economic variables are used as model drivers for the [[energy demand]] model , and non-agricultural water demand contributing to water stress, see ([[Water|Water model]]. To meet the requirements of the household energy demand model, average income is broken down into urban and rural population, and each population into quintiles of income levels. The latter is derived from the assumed uneven income distribution using the [[GINI coefficient|GINI]] factor, a measure of income disparity in a population. The macro indicator GDP per capita is also used directly in IMAGE components, such as [[Human development|human health]], [[flood risks]], and [[nutrients]] (for calculating urban wastewater). The agriculture model [[MAGNET model|MAGNET]] is an economy-wide computable general equilibrium ({{abbrTemplate|CGE}}) model that reproduces exogenous GDP growth projections made in less complex economic growth models, see [[Agricultural economy]]. | In IMAGE 3.0, economic variables are used as model drivers for the [[energy demand]] model , and non-agricultural water demand contributing to water stress, see ([[Water|Water model]]. To meet the requirements of the household energy demand model, average income is broken down into urban and rural population, and each population into quintiles of income levels. The latter is derived from the assumed uneven income distribution using the [[GINI coefficient|GINI]] factor, a measure of income disparity in a population. The macro indicator GDP per capita is also used directly in IMAGE components, such as [[Human development|human health]], [[flood risks]], and [[nutrients]] (for calculating urban wastewater). The agriculture model [[MAGNET model|MAGNET]] is an economy-wide computable general equilibrium ({{abbrTemplate|CGE}}) model that reproduces exogenous GDP growth projections made in less complex economic growth models, see [[Agricultural economy]]. | ||
Revision as of 15:26, 16 June 2016
Parts of Drivers/Scenario drivers
| Projects/Applications |
| Models/Databases |
| Relevant overviews |
| Key publications |
| References |