Atmospheric composition and climate/Policy issues: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
Oostenrijr (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
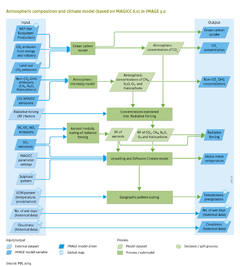
The slow temporal dynamics of the climate system play an important role in climate policy assessments. IMAGE calculations show considerable time lag between policy introduction and impacts on climate change. Even if emissions were substantially reduced from 2020 and onwards, several decades would elapse before stabilization in temperature in the global climate system is observed (Figure above). In addition to these standard climate measures, a range of policy interventions may play a role in the temporal dynamics of the climate system, and may be analysed using the IMAGE system: | The slow temporal dynamics of the climate system play an important role in climate policy assessments. IMAGE calculations show considerable time lag between policy introduction and impacts on climate change. Even if emissions were substantially reduced from 2020 and onwards, several decades would elapse before stabilization in temperature in the global climate system is observed (Figure above). In addition to these standard climate measures, a range of policy interventions may play a role in the temporal dynamics of the climate system, and may be analysed using the IMAGE system: | ||
* Mitigation in short-lived versus long-lived greenhouse gas emissions, and co-benefits with air pollution measures ([[Shindell et al., 2012]]). Short-term benefits in air quality and climate mitigation may be achieved by reducing black carbon emissions and ozone precursors. | * Mitigation in short-lived versus long-lived greenhouse gas emissions, and co-benefits with air pollution measures ([[Shindell et al., 2012]]). Short-term benefits in air quality and climate mitigation may be achieved by reducing black carbon emissions and ozone precursors. | ||
* Non-mitigation management of global radiative forcing, such as by means of geo-engineering as shown in | * Non-mitigation management of global radiative forcing, such as by means of geo-engineering as shown in the figure below ([[Van Vuuren and Stehfest, 2013]]). | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 09:04, 24 June 2014
Parts of Atmospheric composition and climate/Policy issues
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
| References |