Climate policy/Data uncertainties limitations: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ComponentDataUncertaintyAndLimitationsTemplate | {{ComponentDataUncertaintyAndLimitationsTemplate | ||
|Reference=Enerdata, 2010; Kindermann et al., 2008; | |Reference=Enerdata, 2010; Kindermann et al., 2008; | ||
|Description=<h2> Data uncertainties and limitations </h2> | |Description=<h2> Data uncertainties and limitations </h2> | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
===Uncertainties=== | ===Uncertainties=== | ||
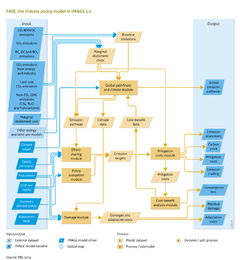
Each FAIR module has uncertainties. The main uncertainties in the cost modules are future business-as-usual emission trends (higher emission trends imply higher mitigation costs to achieve a certain target) and MAC curves (difficult to estimate the costs of reducing emissions far into the future). In the Global Pathfinder and Climate module, uncertainty in the climate sensitivity of the climate system to greenhouse gas concentration is an key source of uncertainty but can be covered by using a probabilistic version of the [[MAGICC model|MAGICC]] climate model. Probably the largest source of uncertainty relates to climate change damage, as there are few studies on the economic damage of climate change on a global or regional scale. | |||
<div class=“version changev31”> | |||
Each FAIR module has uncertainties. The main uncertainties in the cost modules are future business-as-usual emission trends (higher emission trends imply higher mitigation costs to achieve a certain target) and MAC curves (difficult to estimate the costs of reducing emissions far into the future). In the Global Pathfinder FAIRSiMCaP and Climate module, uncertainty in the climate sensitivity of the climate system to greenhouse gas concentration is an key source of uncertainty but can be covered by using a probabilistic version of the [[MAGICC model|MAGICC]] climate model. Probably the largest source of uncertainty relates to climate change damage, as there are few studies on the economic damage of climate change on a global or regional scale. | |||
===Limitations=== | ===Limitations=== | ||
A key limitation of the Global Pathfinder and Climate module is that the costs of climate policy are not fed back to the rest of the economy. Furthermore, some abatement technologies especially in the land system are assumed to have no effects on other parameters, such as crop yields. Some land-based mitigation technologies such as afforestation, and agricultural carbon management, are included in FAIR, but are not represented explicitly in the terrestrial vegetation system of the IMAGE framework. | |||
A key limitation of the Global Pathfinder module FAIRSiMCaP and Climate module is that the costs of climate policy are not fed back to the rest of the economy. Furthermore, some abatement technologies especially in the land system are assumed to have no effects on other parameters, such as crop yields. Some land-based mitigation technologies such as afforestation, and agricultural carbon management, are included in FAIR, but are not represented explicitly in the terrestrial vegetation system of the IMAGE framework. | |||
</div> | |||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 20:46, 6 November 2016
Parts of Climate policy/Data uncertainties limitations
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |