Atmospheric composition and climate/Description: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "Nutrients" to "Nutrient balances") |
m (Text replace - "Crop and grassland model" to "Crop and grass") |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
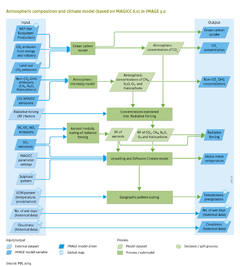
The energy fluxes simulated by MAGICC include heat transport from the atmosphere, through the mixing top layer of the ocean, to lower water layers (60 layers), and heat transfer between land and ocean. Due to the slow heat transport to the ocean, it takes a long time until the earth's temperature is in a new equilibrium following a change in radiative forcing. The parameters of the MAGICC model that control heat transport and final global mean temperature change are calibrated to reproduce the results of 19 Global Circulation Models of AR4 ([[Meinshausen et al., 2011b]]). Next to these 19 alternative [[AOGCM model|AOGCM]]-specific sets of parameters, also a ‘medium’ parameterisation is available, which results in a behaviour that represents the mean of these 19 model emulations. | The energy fluxes simulated by MAGICC include heat transport from the atmosphere, through the mixing top layer of the ocean, to lower water layers (60 layers), and heat transfer between land and ocean. Due to the slow heat transport to the ocean, it takes a long time until the earth's temperature is in a new equilibrium following a change in radiative forcing. The parameters of the MAGICC model that control heat transport and final global mean temperature change are calibrated to reproduce the results of 19 Global Circulation Models of AR4 ([[Meinshausen et al., 2011b]]). Next to these 19 alternative [[AOGCM model|AOGCM]]-specific sets of parameters, also a ‘medium’ parameterisation is available, which results in a behaviour that represents the mean of these 19 model emulations. | ||
The global mean temperature change from MAGICC, and maps of temperature and precipitation change are used in a pattern scaling, to derive spatially explicit temperature and precipitation changes in every time step, which may subsequently be used by various other IMAGE modules (on [[C cycle and natural vegetation dynamics]], [[Crop and | The global mean temperature change from MAGICC, and maps of temperature and precipitation change are used in a pattern scaling, to derive spatially explicit temperature and precipitation changes in every time step, which may subsequently be used by various other IMAGE modules (on [[C cycle and natural vegetation dynamics]], [[Crop and grass]], [[Hydrological cycle]], [[Nutrient balances]]). Based on grid-specific temperature and precipitation changes and corresponding changes in global mean temperature (2071–2100 compared to 1961–1990) from AR4’s AOGCM model results (Ref database), the global mean temperature change in each time step is used to calculate grid-specific temperature and precipitation changes via linear interpolation. For future calculations, the results of AR5 should be used to update the MAGICC parameterisation for all available AOGCMs, and to update the gridded patterns of climate change. | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 16:21, 11 December 2013
Parts of Atmospheric composition and climate/Description
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
| References |