Livestock systems/Description: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
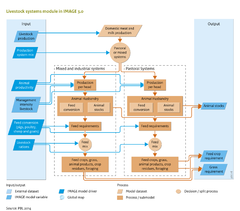
|Description=For each world region, IMAGE distinguishes two livestock production systems, namely pastoral systems and mixed/industrial systems, on the basis of [[FAO]] studies ([[Seré and Steinfeld, 1996]]). In general, pastoral systems are dominated by extensive ruminant production systems. Mixed and industrial systems are more intensive than pastoral ones, and animal husbandry comprises grazing ruminants and monogastrics. For years up to the present, the distribution of livestock production over the two systems, for each IMAGE region, is constructed from historical data, whereas for future years, this depends on the scenario selected. | |Description=For each world region, IMAGE distinguishes two livestock production systems, namely pastoral systems and mixed/industrial systems, on the basis of [[FAO]] studies ([[Seré and Steinfeld, 1996]]). In general, pastoral systems are dominated by extensive ruminant production systems. Mixed and industrial systems are more intensive than pastoral ones, and animal husbandry comprises grazing ruminants and monogastrics. For years up to the present, the distribution of livestock production over the two systems, for each IMAGE region, is constructed from historical data, whereas for future years, this depends on the scenario selected. | ||
IMAGE distinguishes five animal categories: beef and dairy cattle (large ruminants), goats and sheep as one group (small ruminants) and pigs and poultry (monogastrics). The numbers of animals and their shares per production system are calculated from data on domestic livestock production, per region, provided by the agricultural economy model ([[Agricultural economy and forestry]]) (see figure on the right). The number of animals per category is calculated from the total production per region and per animal specific to that region. Stocks of dairy cows ([[HasAcronym::POP]]), per country or world region, are obtained from total milk production ([[HasAcronym::PROD]]) and the milk production per animal ([[HasAcronym::MPH]]): | IMAGE distinguishes five animal categories: beef and dairy cattle (large ruminants), goats and sheep as one group (small ruminants) and pigs and poultry (monogastrics). The numbers of animals and their shares per production system are calculated from data on domestic livestock production, per region, provided by the agricultural economy model ([[Agricultural economy and forestry]]) (see figure on the right). The number of animals per category is calculated from the total production per region and per animal specific to that region. Stocks of dairy cows ([[HasAcronym::POP]]), per country or world region, are obtained from total milk production ([[HasAcronym::PROD]]) and the milk production per animal ([[HasAcronym::MPH]]): | ||
{{FormulaAndTableTemplate|Formula1_LS}} | {{FormulaAndTableTemplate|Formula1_LS,240}} | ||
Animal stocks per region, for the categories beef cattle, pigs, and sheep and goats, is obtained from production and carcass weight ([[HasAcronym::CW]]) and off-take rate ([[HasAcronym::OR]]): | Animal stocks per region, for the categories beef cattle, pigs, and sheep and goats, is obtained from production and carcass weight ([[HasAcronym::CW]]) and off-take rate ([[HasAcronym::OR]]): | ||
{{FormulaAndTableTemplate|Formula2_LS}} | {{FormulaAndTableTemplate|Formula2_LS}} | ||
Revision as of 10:40, 16 December 2013
Parts of Livestock systems/Description
| Component is implemented in: |
| Components: |
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
|
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
| References |