Atmospheric composition and climate/Policy issues: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
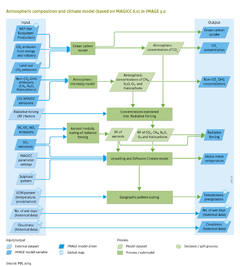
The slow temporal dynamics of the climate system play an important role in climate policy assessments. IMAGE calculations show considerable time lag between policy introduction and impacts on climate change. Even if emissions were substantially reduced from 2020 and onwards, several decades would elapse before reduction in temperature in the global climate system is observed (see figure below). In addition to these standard climate measures, a range of policy interventions may play a role in the temporal dynamics of the climate system, and may be analysed using the IMAGE system: | The slow temporal dynamics of the climate system play an important role in climate policy assessments. IMAGE calculations show considerable time lag between policy introduction and impacts on climate change. Even if emissions were substantially reduced from 2020 and onwards, several decades would elapse before reduction in temperature in the global climate system is observed (see figure below). In addition to these standard climate measures, a range of policy interventions may play a role in the temporal dynamics of the climate system, and may be analysed using the IMAGE system: | ||
[[**interventions...]] | |||
In the policy scenarios, emissions decrease substantially after 2020 but concentration levels only decrease or stabilise after 2050. Because of inertia in the climate system, global mean temperature will not stabilise until the end of this century under the most ambitious climate policy scenario (2.6 W/m2). | |||
In addition to conventional climate policy, some situations may require urgent action on climate change, either rapid mitigation or solar radiation management (SRM) such as sulphur emissions to the stratosphere. Radiative forcing is immediately stabilised at the intended level by SRM, and temperatures are also adjusted immediately (though not yet at equilibrium level), and even faster under extreme SRM than would be possible through strong mitigation. However, substantial uncertainties and risks are related to such drastic manipulations of the radiation balance. | |||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 15:58, 10 February 2014
Parts of Atmospheric composition and climate/Policy issues
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
| References |