Emissions/Description: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
The emission factor approach is used to calculate energy emissions and several land-use related emissions. Following the equation above, there is a direct relation between the level of economic activity and emission level. Also shifts in economic activity (e.g. use of natural gas instead of coal) may influence the total emissions. Finally, emissions can change as result of changes in the emission factors (EF) or climate policy (AF). Some generic rules are used to describe the changes of emissions over time (see further). The abatement factor (AF) are determined in the climate policy model [[FAIR model|FAIR]] (see [[Climate policy]]). The emission factor approach has some limitations, most importantly that is limited in capturing the consequences of specific emission control technology (or management action) for multiple species (either synergies or trade-offs). | The emission factor approach is used to calculate energy emissions and several land-use related emissions. Following the equation above, there is a direct relation between the level of economic activity and emission level. Also shifts in economic activity (e.g. use of natural gas instead of coal) may influence the total emissions. Finally, emissions can change as result of changes in the emission factors (EF) or climate policy (AF). Some generic rules are used to describe the changes of emissions over time (see further). The abatement factor (AF) are determined in the climate policy model [[FAIR model|FAIR]] (see [[Climate policy]]). The emission factor approach has some limitations, most importantly that is limited in capturing the consequences of specific emission control technology (or management action) for multiple species (either synergies or trade-offs). | ||
* ''Emission factor method with spatial distribution'' (GEF) represents a special case of the EF method where a proxy distribution is used to present gridded emissions. This is done for a number of sources, for example emissions from animals ([[ | * ''Emission factor method with spatial distribution'' (GEF) represents a special case of the EF method where a proxy distribution is used to present gridded emissions. This is done for a number of sources, for example emissions from animals ([[Emissions#Inputs|table]]). | ||
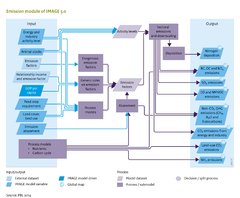
* ''Process model''. (GPM). Land-use related emissions of NH3, N2O and NO are calculated with grid-specific models. The models included in IMAGE are simple regression models that generate an emission factor (see flowchart on the right). It should be noted that for comparison with other models, IMAGE also includes the N2O methodology as proposed by [[IPCC]] ([[IPCC, 2006]]). | * ''Process model''. (GPM). Land-use related emissions of NH3, N2O and NO are calculated with grid-specific models. The models included in IMAGE are simple regression models that generate an emission factor (see flowchart on the right). It should be noted that for comparison with other models, IMAGE also includes the N2O methodology as proposed by [[IPCC]] ([[IPCC, 2006]]). | ||
Revision as of 15:27, 15 January 2014
Parts of Emissions/Description
| Component is implemented in: |
Components:and
|
| Projects/Applications |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
| References |
|