Energy conversion: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
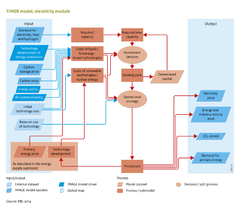
|Description=Energy from primary sources often has to be converted into secondary energy carriers that are more easily accessible for final consumption, for example the production of electricity and hydrogen, oil products from crude oil in refineries, and fuels from biomass. Studies on transitions to more sustainable energy systems also show the importance of these conversions for the future. | |Description=Energy from primary sources often has to be converted into secondary energy carriers that are more easily accessible for final consumption, for example the production of electricity and hydrogen, oil products from crude oil in refineries, and fuels from biomass. Studies on transitions to more sustainable energy systems also show the importance of these conversions for the future. | ||
The energy conversion module of TIMER simulates the choices of input energy carriers in two steps. In the first step, investment decisions are made on the future generation mix in terms of newly added capital. In the second step, the actual use of the capacity in place depends on a set of model rules that determine the purpose and how frequently the different types of power plants are used (baseload/peakload). The discussion focuses on the production of electricity and hydrogen. Other conversion processes have only be implemented in the model by simple multipliers, as they mostly convert energy from a single primary source to one secondary energy carrier. These processes are discussed in [[Energy supply| | The energy conversion module of TIMER simulates the choices of input energy carriers in two steps. In the first step, investment decisions are made on the future generation mix in terms of newly added capital. In the second step, the actual use of the capacity in place depends on a set of model rules that determine the purpose and how frequently the different types of power plants are used (baseload/peakload). The discussion focuses on the production of electricity and hydrogen. Other conversion processes have only be implemented in the model by simple multipliers, as they mostly convert energy from a single primary source to one secondary energy carrier. These processes are discussed in [[Energy supply|Energy Supply.]]. | ||
|ComponentCode=EC | |ComponentCode=EC | ||
|AggregatedComponent=Energy supply and demand | |AggregatedComponent=Energy supply and demand | ||
|FrameworkElementType=pressure component | |FrameworkElementType=pressure component | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 17:31, 8 May 2014
Parts of Energy conversion
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
Key policy issues
- What is the potential role of energy conversion sector, particularly in power production, in achieving a more sustainable energy system?
- What are the potential roles of individual technologies, such as carbon capture and storage (CCS), nuclear power, hydrogen and renewable energy?