Emissions: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "CO2 emission;" to "CO2 emission from energy and industry;") |
m (Text replace - "Non CO2 GHG emissions (CH4,N2O, Halocarbon);" to "Non CO2 GHG emissions (CH4, N2O, Halocarbon);") |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|KeyReference=Braspenning Radu et al., 2012; Harnisch et al., 2009; Van Vuuren et al., 2006; | |KeyReference=Braspenning Radu et al., 2012; Harnisch et al., 2009; Van Vuuren et al., 2006; | ||
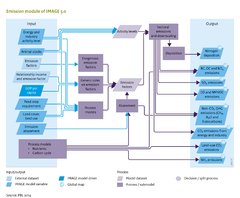
|InputVar=Industry value added; Activity level; Sector value added; Feed crop requirements; Animal stock; Land cover; N and P soil budget; Emission abatement; | |InputVar=Industry value added; Activity level; Sector value added; Feed crop requirements; Animal stock; Land cover; N and P soil budget; Emission abatement; | ||
|OutputVar=CO2 emission from energy and industry; CO, NMVOC emissions; Non CO2 GHG emissions (CH4,N2O, Halocarbon); Nitrogen deposition; Ammonia (NH3) loss; BC, OC, NOx emissions; SO2 emission; | |OutputVar=CO2 emission from energy and industry; CO, NMVOC emissions; Non CO2 GHG emissions (CH4, N2O, Halocarbon); Nitrogen deposition; Ammonia (NH3) loss; BC, OC, NOx emissions; SO2 emission; | ||
|Parameter=Exogenous emission factors; Relationship income and emission factor; Relationship livestock feed category and emission rate; | |Parameter=Exogenous emission factors; Relationship income and emission factor; Relationship livestock feed category and emission rate; | ||
|Description=Emissions of greenhouse gases and air pollutants are an important cause of environmental problems such as climate change, acidification, eutrophication, urban air pollution and water pollution. Better understanding the drivers of these emissions and the different ways to abate them is therefore important to assess global environmental problems. Greenhouse gas and air pollutant emiissions stem from a range of sources, both anthropogenic and natural ones. The former category includes energy consumption and production, industrial processes, agriculture and land use change. The latter include wetlands, oceans and unmanaged land. In this chapter we provide a description of the approaches used in IMAGE to calculate emissions from a variety of sources and sectors in a consistent manner. | |Description=Emissions of greenhouse gases and air pollutants are an important cause of environmental problems such as climate change, acidification, eutrophication, urban air pollution and water pollution. Better understanding the drivers of these emissions and the different ways to abate them is therefore important to assess global environmental problems. Greenhouse gas and air pollutant emiissions stem from a range of sources, both anthropogenic and natural ones. The former category includes energy consumption and production, industrial processes, agriculture and land use change. The latter include wetlands, oceans and unmanaged land. In this chapter we provide a description of the approaches used in IMAGE to calculate emissions from a variety of sources and sectors in a consistent manner. | ||
Revision as of 10:05, 30 January 2014
Parts of Emissions
| Component is implemented in: |
Components:and
|
| Projects/Applications |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
Key policy issues
- How will emissions of greenhouse gases and air pollutants develop in scenarios with and without policy interventions, such as climate policy and air pollution control?
- What synergies between climate policy and air pollution control can be identified?
Introduction