Energy conversion/Description: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Oostenrijr (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Oostenrijr (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
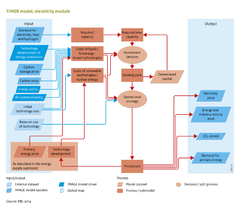
The cost of one unit electricity generated is equal to the sum of the capital cost, operational and maintenance costs (O&M), fuel cost, and CO<sub>2</sub> storage cost. | The cost of one unit electricity generated is equal to the sum of the capital cost, operational and maintenance costs (O&M), fuel cost, and CO<sub>2</sub> storage cost. | ||
See the additional info on [[Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)]]. | See the additional info on [[Grid and infrastructure]] and [[Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)]]. | ||
====Solar and wind power==== | ====Solar and wind power==== | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
#Intermittence does not play an important role because hydrogen can be stored to some degree. Thus, there are no equations simulating system integration. | #Intermittence does not play an important role because hydrogen can be stored to some degree. Thus, there are no equations simulating system integration. | ||
#Hydrogen can be traded. A trade model is added, similar to those for fossil fuels described in [[Energy supply]]. | #Hydrogen can be traded. A trade model is added, similar to those for fossil fuels described in [[Energy supply]]. | ||
See the additional info on [[Grid and infrastructure]]. | |||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 13:58, 10 August 2015
Parts of Energy conversion/Description
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
| References |