Energy conversion: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "Drivers" to "Scenario drivers") |
m (Text replace - "Land use allocation-Agricultural systems" to "Agricultural systems") |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
|Status=Publishable | |Status=Publishable | ||
|Application=Resource Efficiency | |Application=Resource Efficiency | ||
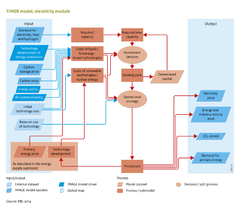
|IMAGEComponent=Energy supply and demand; Energy demand; Energy supply; | |IMAGEComponent=Energy supply and demand; Energy demand; Energy supply; Agricultural systems; Climate policy; Scenario drivers; | ||
|KeyReference=Hoogwijk et al., 2007; Hendriks et al., 2004a; | |KeyReference=Hoogwijk et al., 2007; Hendriks et al., 2004a; | ||
|InputVar=Technology development; Energy policies; Air pollution policies; Demand for electricity and hydrogen; Primary energy price; Carbon storage cost; Carbon price; | |InputVar=Technology development; Energy policies; Air pollution policies; Demand for electricity and hydrogen; Primary energy price; Carbon storage cost; Carbon price; | ||
Revision as of 17:37, 11 December 2013
Parts of Energy conversion
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
Key policy issues
- What is the potential role of energy conversion sector, particularly in power production, in achieving a more sustainable energy system?
- What are the potential roles of individual technologies, such as carbon capture and storage (CCS), nuclear power, hydrogen and renewable energy?