Energy conversion: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
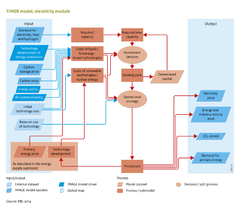
|IMAGEComponent=Energy supply and demand; Energy demand; Energy supply; Land-use allocation; Climate policy; Drivers; | |IMAGEComponent=Energy supply and demand; Energy demand; Energy supply; Land-use allocation; Climate policy; Drivers; | ||
|Model-Database=Enerdata Global Energy & CO2 Data; IEA database; WEC-Uranium; | |Model-Database=Enerdata Global Energy & CO2 Data; IEA database; WEC-Uranium; | ||
|KeyReference=Hoogwijk et al., 2007; Hendriks et al., 2004a; De Boer and Van Vuuren, under review; | |KeyReference=Hoogwijk et al., 2007; Hendriks et al., 2004a; De Boer and Van Vuuren, under review; | ||
|InputVar=Energy policy; Air pollution policy; Demand for electricity, heat and hydrogen; Primary energy price; Carbon storage price; Carbon price; Technology development of energy conversion; | |InputVar=Energy policy; Air pollution policy; Demand for electricity, heat and hydrogen; Primary energy price; Carbon storage price; Carbon price; Technology development of energy conversion; | ||
|Parameter=Initial technology cost; Rules on use of technology; | |Parameter=Initial technology cost; Rules on use of technology; | ||
Revision as of 11:35, 11 November 2016
Parts of Energy conversion
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Models/Databases |
| Key publications |
Key policy issues
- What is the potential role of energy conversion sector, particularly in power production, in achieving a more sustainable energy system?
- What are the potential roles of individual technologies, such as carbon capture and storage (CCS), nuclear power, hydrogen and renewable energy?