Agricultural economy/Description: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
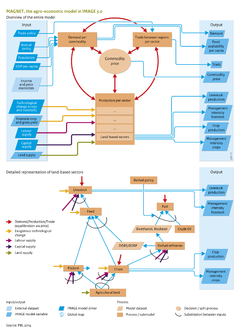
=== Demand and supply === | === Demand and supply === | ||
Household demand for agricultural products is calculated as a function of income, income elasticities, price elasticities, and cross-price elasticities. Income elasticities for agricultural commodities are consistent with FAO estimates ([[Britz, 2003]]), and dynamically depend on purchasing power parity corrected GDP per capita. The supply of all commodities is modelled by an input–output structure that explicitly links the production of goods and services for final consumption via different stages of processing back to primary goods (crops and livestock products) and resources. At each production level, input of labour, capital, and intermediate input or resources (e.g. land) can substitute each other. For example, labour, capital and land are input factors in crop production, and substitution of these production factors is driven by changes in their relative prices. If the price of one input factor increases, it is substituted by other factors, following the price elasticity of substitution. | Household demand for agricultural products is calculated as a function of income, income elasticities, price elasticities, and cross-price elasticities. Income elasticities for agricultural commodities are consistent with [[FAO]] estimates ([[Britz, 2003]]), and dynamically depend on purchasing power parity corrected [[GDP per capita]]. The supply of all commodities is modelled by an input–output structure that explicitly links the production of goods and services for final consumption via different stages of processing back to primary goods (crops and livestock products) and resources. At each production level, input of labour, capital, and intermediate input or resources (e.g. land) can substitute each other. For example, labour, capital and land are input factors in crop production, and substitution of these production factors is driven by changes in their relative prices. If the price of one input factor increases, it is substituted by other factors, following the price elasticity of substitution. | ||
=== Regional aggregation and trade === | === Regional aggregation and trade === | ||
Revision as of 15:43, 16 December 2013
Parts of Agricultural economy/Description
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Key publications |
| References |