Agricultural economy/Description: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|Reference=Hertel, 1997; Britz, 2003; Armington, 1969; Huang et al., 2004; Helming et al., 2010; Banse et al., 2008; | |Reference=Hertel, 1997; Britz, 2003; Armington, 1969; Huang et al., 2004; Helming et al., 2010; Banse et al., 2008; | ||
|Description=<h2>Model description Agricultural economy and forestry</h2> | |Description=<h2>Model description Agricultural economy and forestry</h2> | ||
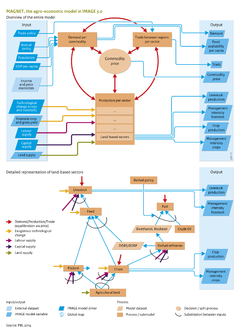
The MAGNET model ([[Woltjer et al., 2011]]) is based on the standard GTAP model ([[Hertel, 1997]]), which is a multi-regional, static, applied computable general equilibrium (CGE) model based on neoclassical microeconomic theory. Although it covers the entire economy, there is a special focus on agricultural sectors. The MAGNET model is a further development of GTAP regarding land use, household consumption, livestock, food, feed and energy crop production, and emission reduction cost calculations. | The MAGNET model ([[Woltjer et al., 2011]]) is based on the standard GTAP model ([[Hertel, 1997]]), which is a multi-regional, static, applied computable general equilibrium ([[CGE]]) model based on neoclassical microeconomic theory. Although it covers the entire economy, there is a special focus on agricultural sectors. The MAGNET model is a further development of GTAP regarding land use, household consumption, livestock, food, feed and energy crop production, and emission reduction cost calculations. | ||
=== Demand and supply === | === Demand and supply === | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
=== Regional aggregation and trade === | === Regional aggregation and trade === | ||
MAGNET is flexible in its regional aggregation (129 regions). For the link with IMAGE, it distinguishes single European countries and, in addition to Europe, 22 large world regions, closely matching the regions in IMAGE (Figure | MAGNET is flexible in its regional aggregation (129 regions). For the link with IMAGE, it distinguishes single European countries and, in addition to Europe, 22 large world regions, closely matching the regions in IMAGE (Figure [[********]] IMAGE regions). Similar to most other CGE models, MAGNET assumes that products traded internationally are differentiated according to country of origin, i.e. domestic and foreign products are not fully identical, but are imperfect substitutes (the so-called Armington assumption ([[Armington, 1969]])). | ||
===Land use=== | ===Land use=== | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
===Reduced availability of land=== | ===Reduced availability of land=== | ||
By restricting land supply in IMAGE and MAGNET, the models can assess scenarios with additional protected areas, or reduced emissions from deforestation and forest degradation (REDD). | By restricting land supply in IMAGE and MAGNET, the models can assess scenarios with additional protected areas, or reduced emissions from deforestation and forest degradation ([[REDD]]). | ||
===Intensification of crop and pasture production=== | ===Intensification of crop and pasture production=== | ||
Revision as of 13:55, 9 December 2013
Parts of Agricultural economy/Description
| Component is implemented in: |
|
| Related IMAGE components |
| Projects/Applications |
| Key publications |
| References |